Installing OMV7 on a Raspberry PI
Revisions:
February, 3rd, 2024 - Short version for RC1
February, 11th, 2024 - Expanded / Full version.
June, 10th, 2025 - “Do not deviated” FOREWORD and Rasp-PI OS users note.
Introduction
Installing OMV7 on Raspberry PI OS Lite, using a scripted install, is a relatively easy task. This document is a guide for that process.
About this Guide
The purpose and intent of this guide is to provide a walk-through to get Raspberry Pi users (hereafter referred to as an “R-PI”) up and running as quickly and as easily as possible. This guide assumes that users have a working Windows Client for installing and executing the needed utilities. It is also assumed that Mac and Linux desktop users will be able to find, install, and use utilities equivalent to those called out in Prerequisites.
- This is a community document and a work in progress. Input and feedback are welcome and can be sent to: omvguide@gmail.com
| FOREWORD | |
| This guide was written to avoid as many installation pitfalls as is possible to anticipate or predict. With that in mind, please adhere to this guide without deviating in any significant way. Specifically, that means DO NOT preconfigure wireless networking (that will be covered later - after OMV is installed), or use raspi-config prior to the installation of OMV. Once the OMV installation is complete, and after backing the OS' SD-card → Cloning Flash Media, additional configuration or experimentation will be possible without losing the install, if something goes awry. | |
Supported Devices
OMV7 will install on R-PI models 2B and higher. However, in practical terms, the performance of the model 2B is marginal.
Not Supported
- Desktop versions of Raspberry PI OS are NOT supported. (Use the Raspberry PI OS “lite“ version only.)
- Legacy Raspberry PI's
R-PI models earlier than the 2B and the R-PI Zero have not been tested and are not supported. They are far too slow to run a NAS application. Please do not post on OMV's forum, expecting support for these models.
Prerequisites
This installation process requires a wired Ethernet connection and Internet access.
Typically, all that is needed to begin the installation is an Ethernet cable, a power supply sufficient for the R-PI model being used, and one SD-card (two SD-cards are preferred for backup).
| Note | |
|
For best results, please DO NOT vary from the process outlined. Examples of variation would be "preconfiguring wireless networking" or the installation of extra packages before running the installation script. | |
To get started, a few utilities are needed to check the SD-card and install the Raspberry PI OS image.
- Raspberry PI OS images are installed using the Raspberry PI OS imager. Download the appropriate imager → here. (Imager downloads are at the bottom of the page.) The Raspberry PI OS imager is installable on a Windows client.
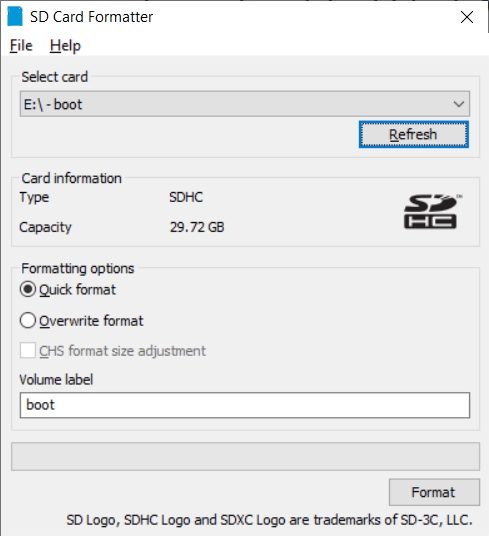
- SDformatter is a utility for formatting SD-cards that does a trim operation on flash media to clear remnants of old deleted files. SDformatter is installable on a Windows client.
- Users will need a utility like 7-Zip to decompress zip archives like the SD-card test program below. 7-Zip is installable on a Windows client.
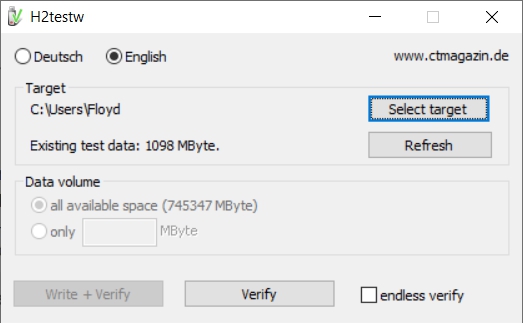
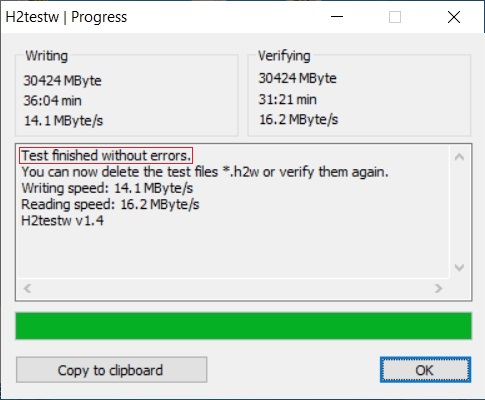
- h2testw_1.4 is a flash media test program. With a freshly formatted SD-card or USB thumbdrive, it writes files with known content and verifies the content in a read operation, detecting errors in the process. h2testw_1.4 downloads as a zip file. By right clicking on the zip file and using “Extract All”, 7-Zip will expand the zip file to a folder named h2testw_1.4 The executable inside this folder is a portable application. Run the executable.
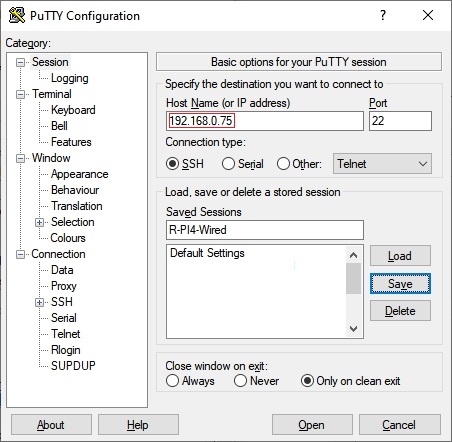
- PuTTY is an SSH client that will allow users to connect to their SBC, from a Windows client, and get on the command line. PuTTY is installable on a Windows client.
- While 8GB is the minimum and will work fine, a 16GB SD-card will provide longer life in the role of a boot drive. Users are encouraged to get two SD-cards. One is for the installation and a second card for backing up the OS installation, when configuration is complete.
For the best experience, use only high quality new SD-cards, such as Samsung or SanDisk, that are rated A1 Class 10 or better.
Format and Test Flash Media
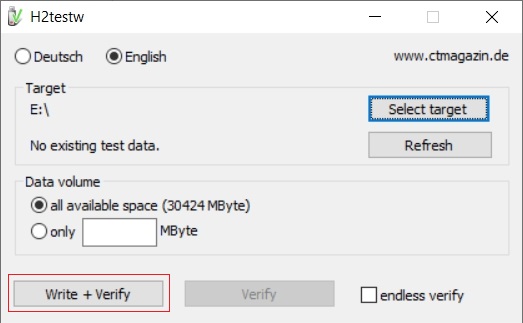
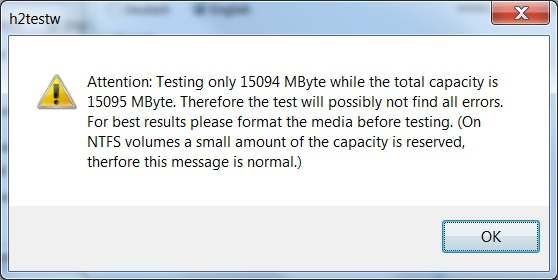
Due to the rise in counterfeit media and media that reports a fake size, it’s recommended that all SD-cards or USB thumbdrives, new or used, be formatted with SDFormatter and tested with h2testw1.4 before using them.
| Note | |
| When an SD-card is inserted and recognized, Windows may offer to format the card several times. Cancel all of these attempts. | |
Burning the Image
Preinstallation Notes
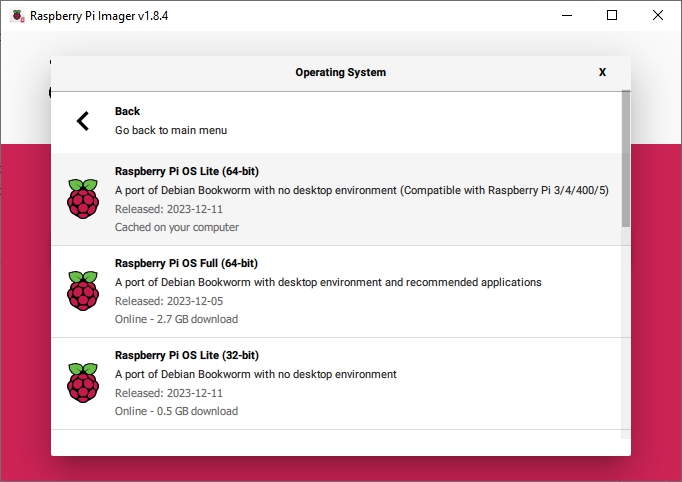
All supported models of Raspberry PI will run the 32bit lite image of Raspberry PI OS. However, when using the 32bit image, model 4's with 8Gb of ram would be limited to using 4Gb of ram for a “single process”. This is not to say that the extra 4Gb of ram is wasted. The additional 4Gb would be distributed among additional processes. However, the 64bit lite version will allow more than 4Gb per process and, in many instances, performance is better / faster.
In any case, users with Raspberry PI models 3 or higher will be well served with 64bit lite version.
Users of Raspberry PI model 2B users should use the 32bit lite image.
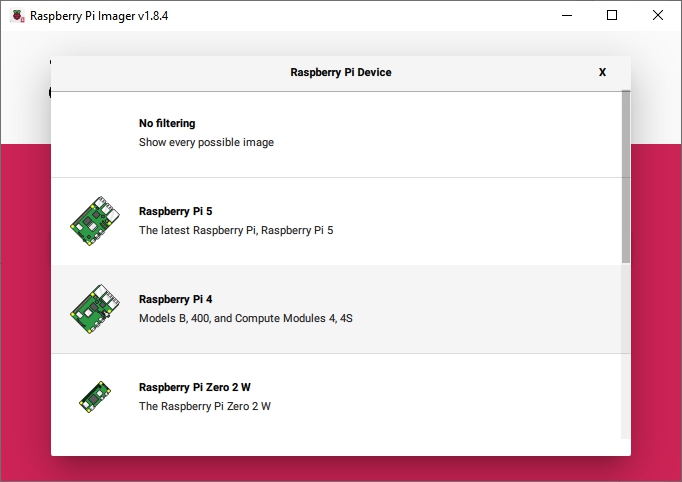
The Raspberry PI OS Imager
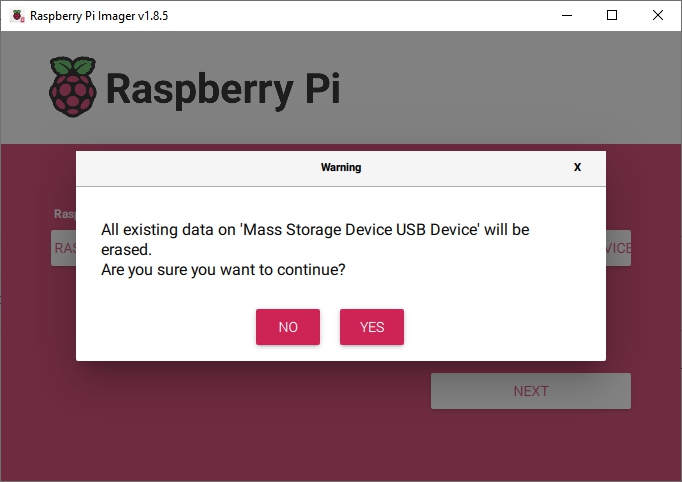
The Raspberry PI Imager is a convenient “all in one” utility for burning Raspberry PI OS onto an SD-card. In the options allowed by the imager, the appropriate image for OMV is selected, the image is downloaded, it's burnt to the SC-card and the image is verified in one step.
| Warning | |
| Do not select "Full" versions of Raspberry PI OS. Desktop versions are not compatible with Openmediavault. | |
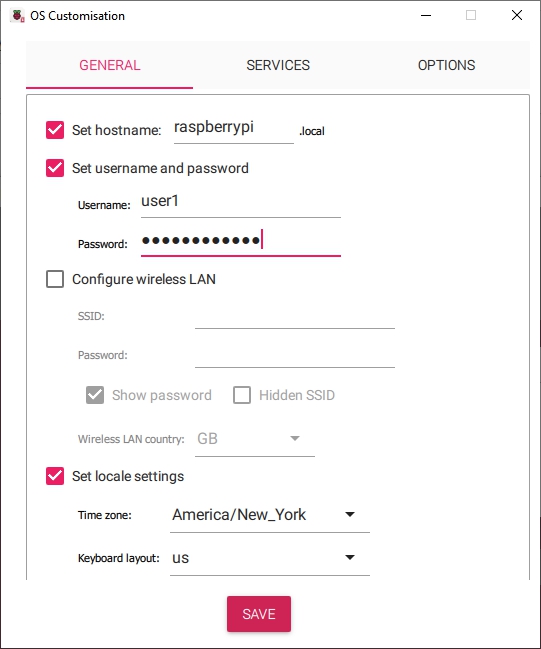
- Check the box for Set Hostname: User's choice - the default is fine.
- Check the box for Set username and password: These entries will create an admin user with SUDO capabilities.
- DO NOT check the box for Configure Wireless Networking: Configuring WiFi will be done later, in OMV's GUI.
- Check the box for Set local settings: Set for the user's time zone.
| Warning | |
|
First: The username, created in this dialog, CAN NOT be admin. admin is reserved for the OMV installation. Second: The OMV application will not be aware of the username installed during the OS flashing process (in this case user1) or the default user created by Raspberry PI OS, pi. Unless they are manually added in OMV's GUI under Users, Users (using the exact same username AND password as used on the CLI), these users will not have access to network shares and other resources within, or created, by OMV. | |
The First Boot
*At this point, a wired Ethernet connection is required to connect to the R-PI, with PuTTY, and to install OMV in a later process.*
- Insure the R-PI is connect to wired Ethernet.
- Insert the SD-card with the Raspberry PI OS image into the R-PI and apply power.
- Wait 3 to 5 minutes.
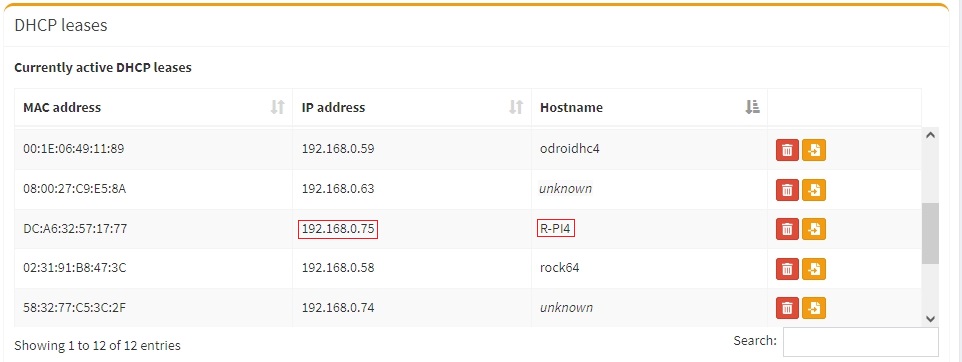
The IP address to use for logging into the console is available from your DHCP server. In most cases, your DHCP server will be running on your LAN's router. Log into your router and look for the IP address associated with your R-PI.
- In the event that an IP address is not issued to your SBC, check the wired Ethernet connection and reboot the device. This may mean unplugging and plugging the power supply back in. Allow time for boot up (5 minutes or so) and check the DHCP server again.
- If an address is not issued, or if the user doesn't know how to find the Raspberry Pi's IP address on their DHCP server, connect a monitor and a USB keyboard to watch the boot process until it completes. If the IP address is not displayed at the end of the boot cycle, login with the user pi using the password raspberry.
- In rare instances, it may be necessary to reboot the LAN's router, followed by rebooting the Raspberry PI.
Once logged in, type ip add on the command line. Note the IP address of the Ethernet interface, in the output, and proceed to First Time Login.
To be able to utilize Copy + Paste: Working with the R-PI using SSH, as detailed in First Time Login, is highly recommended.
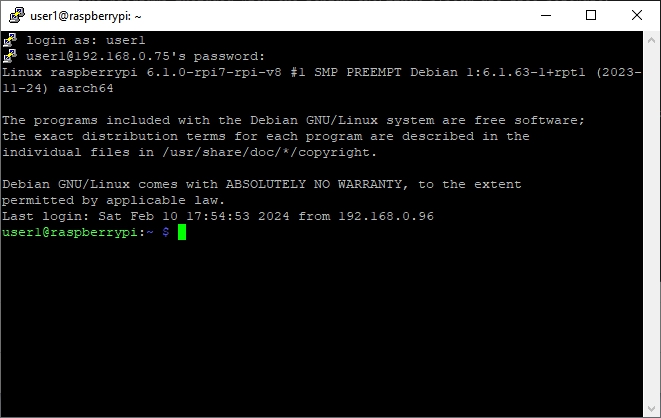
Raspberry PI OS - First Time Logon
Raspberry PI OS Updates and Upgrades
Before installing OMV, update, upgrade and prepare Raspberry PI OS using the following commands:
Copy each of the following commands, one at a time.
Highlight a command and use (Ctrl+C) to copy the full line. Paste the line into PuTTY's SSH window, with a right mouse click. Then hit Enter.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade -y
wget -O - https://github.com/OpenMediaVault-Plugin-Developers/installScript/raw/master/preinstall | sudo bash
When the above commands are complete, type;
sudo reboot
PuTTY will disconnect – this is expected. Wait 3 to 5 minutes and reopen a new PuTTY SSH window and log in again.
| Note | |
|
In the event that the SSH client does not respond to the IP address used during the first boot, look at your DHCP server to see if a “new” IP address has been assigned. In rare cases, the LAN's router / DHCP server may need a reboot. | |
Install OMV
Installing OMV on Raspberry's is very easy, thanks to Arron Murray (ryecoaaron on the OMV Forum) for providing a comprehensive installation script that's executed from a single line.
Copy the following line complete (Ctrl+C) and paste it into PuTTY's SSH window, with a right mouse click. Then hit Enter.
wget -O - https://github.com/OpenMediaVault-Plugin-Developers/installScript/raw/master/install | sudo bash
Once the script is running, click out of the SSH window so the script will not be interrupted.
Do Not close PuTTY – that will terminate the root session. Minimizing PuTTY is OK, but it must be running.
Depending on several factors, running this script may take up to 30 minutes.
When the script is complete, the R-PI will automatically reboot.
First Time GUI Logon
After 3 to 5 minutes, OMV can be logged in using the same IP address that was used for the SSH client, entered in a web browser address bar. The web GUI user is admin and the default password is openmediavault
Note - after the completion of the script:
In the event that the OMV console or SSH client does not respond to the IP address used during the installation, recheck your DHCP server to see if a “new” IP address has been assigned.
(Typically, consumer router DHCP leases last at least 24 hours. In cases where DHCP leases are very short - as it is with some versions of DD-WRT router firmware [10 minutes] - the lease issued to the SBC may time out at the end of the installation. A different address may be issued on reboot.)
Finishing Up
- To add an existing or add-on Wireless Interface to openmediavault, see Final Notes below.
- New users can continue with the setup of OMV using the Getting Started with Openmediavault 7 guide, starting in the section titled → Initial Configuration.
- All users are encouraged to review this resource → Utilities, Maintenance & Backup for an easy process to clone your SBC's SD-Card and for additional information that will help in managing and maintaining an openmediavault server.
Final Notes:
Wireless Networking
First it should be noted that using a wireless interface, with a server, is not the best idea. To prevent a number of issues such as interference, bandwidth contention issues with clients, etc., a server should be connected to the wired LAN ports of a router or a network switch. However it is understood that, in some cases, wired connections may not be an option.
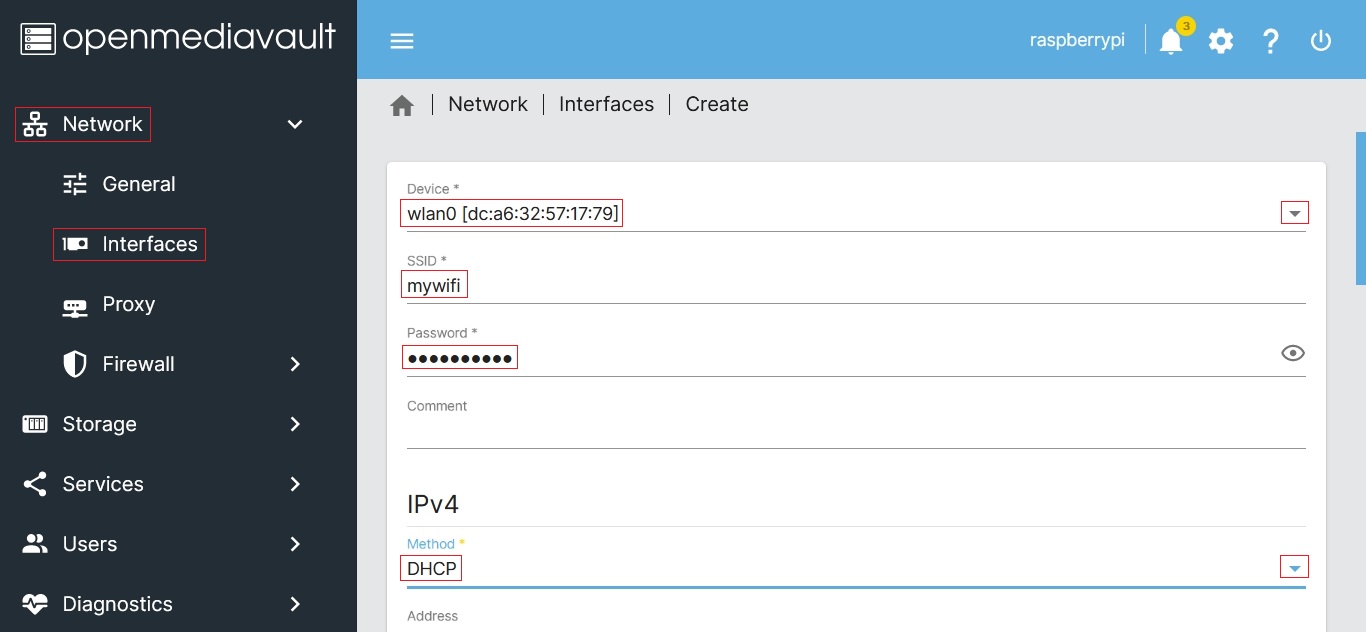
If your R-PI is equipped with a wireless interface, by default, OMV will not show it in the GUI but it can be added.
- An existing interface can be added as noted in the following.
- After plugging it in, a compatible add-on USB wireless interface can be added in the same manner.
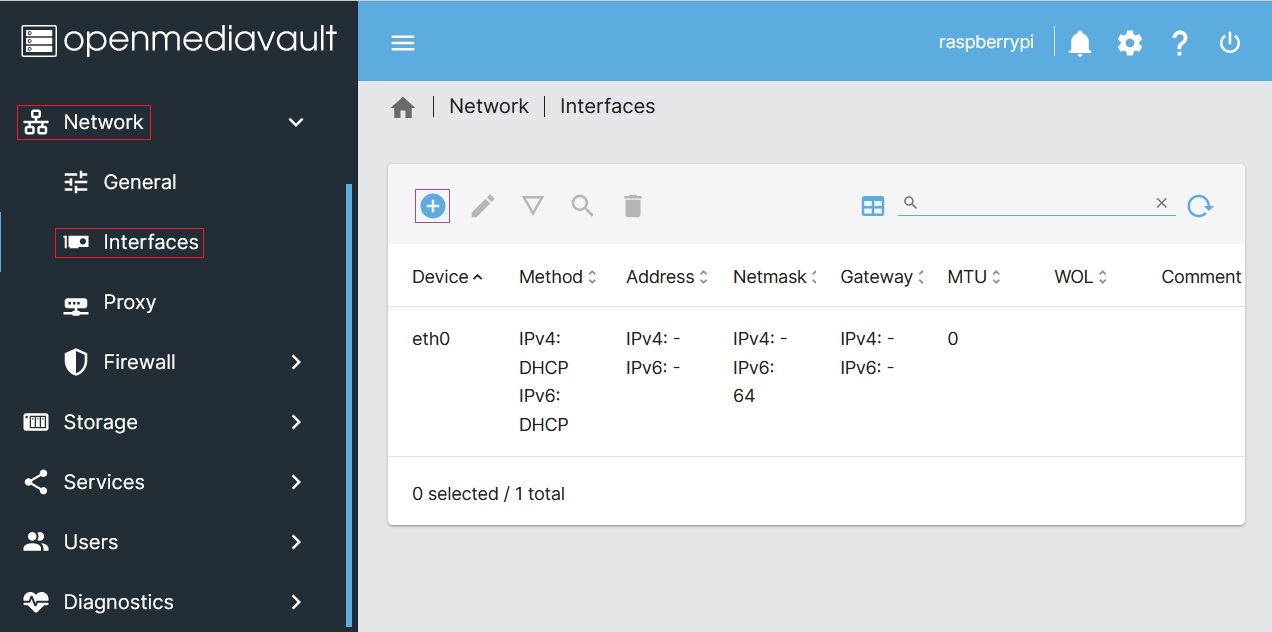
At this point, the wireless interface will appear under Network, in the Interfaces window. Further configuration can be done, as needed, by clicking on the interface line and the edit button (pencil).
A Closing Note
We, who support the openmediavault project, hope that you’ll find your openmediavault server to be
enjoyable, efficient, and easy to use.
If you found this guide to be helpful, please consider a modest donation to support the
hosting costs of this server (OMV-Extras) and the project (Openmediavault).
OMV-Extras.org
www.openmediavault.org
Venmo: ryecoaaron